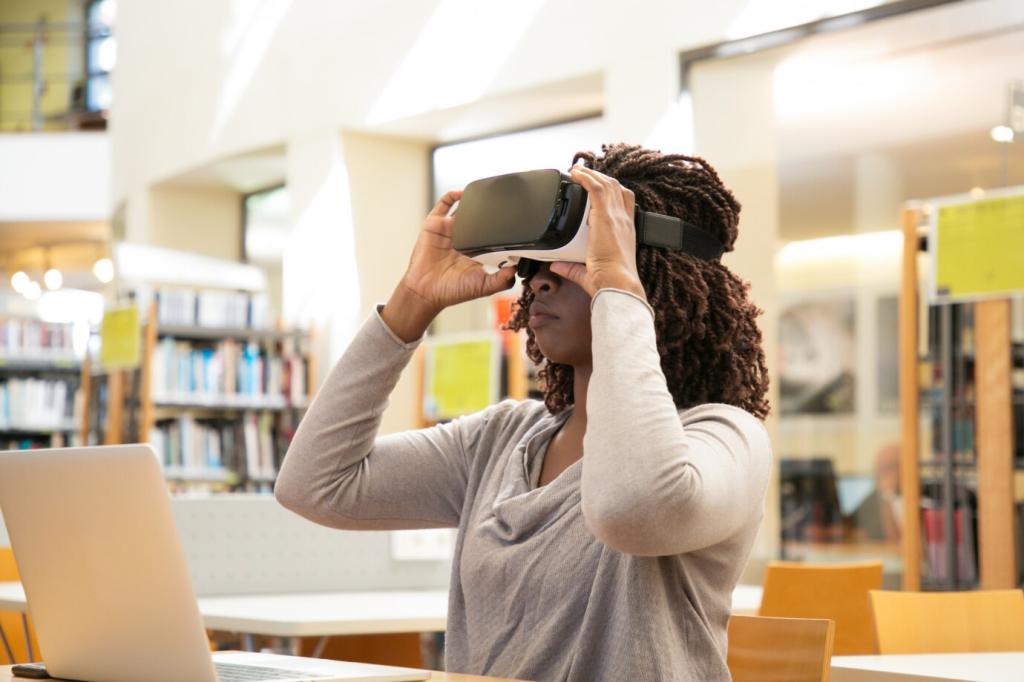
VR Technologies Transforming Language Classrooms
Virtual Reality (VR) is revolutionizing language education by creating immersive, interactive experiences that mimic real-life communication scenarios. In language classrooms worldwide, VR technologies are fostering a dynamic, engaging, and highly effective learning environment. By bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, VR enables students to practice language skills in authentic settings without the limitations of physical location or traditional resources. This transformative approach holds the potential to reshape how languages are taught and learned, making the process not only more enjoyable but significantly more impactful.
Immersive Language Experiences
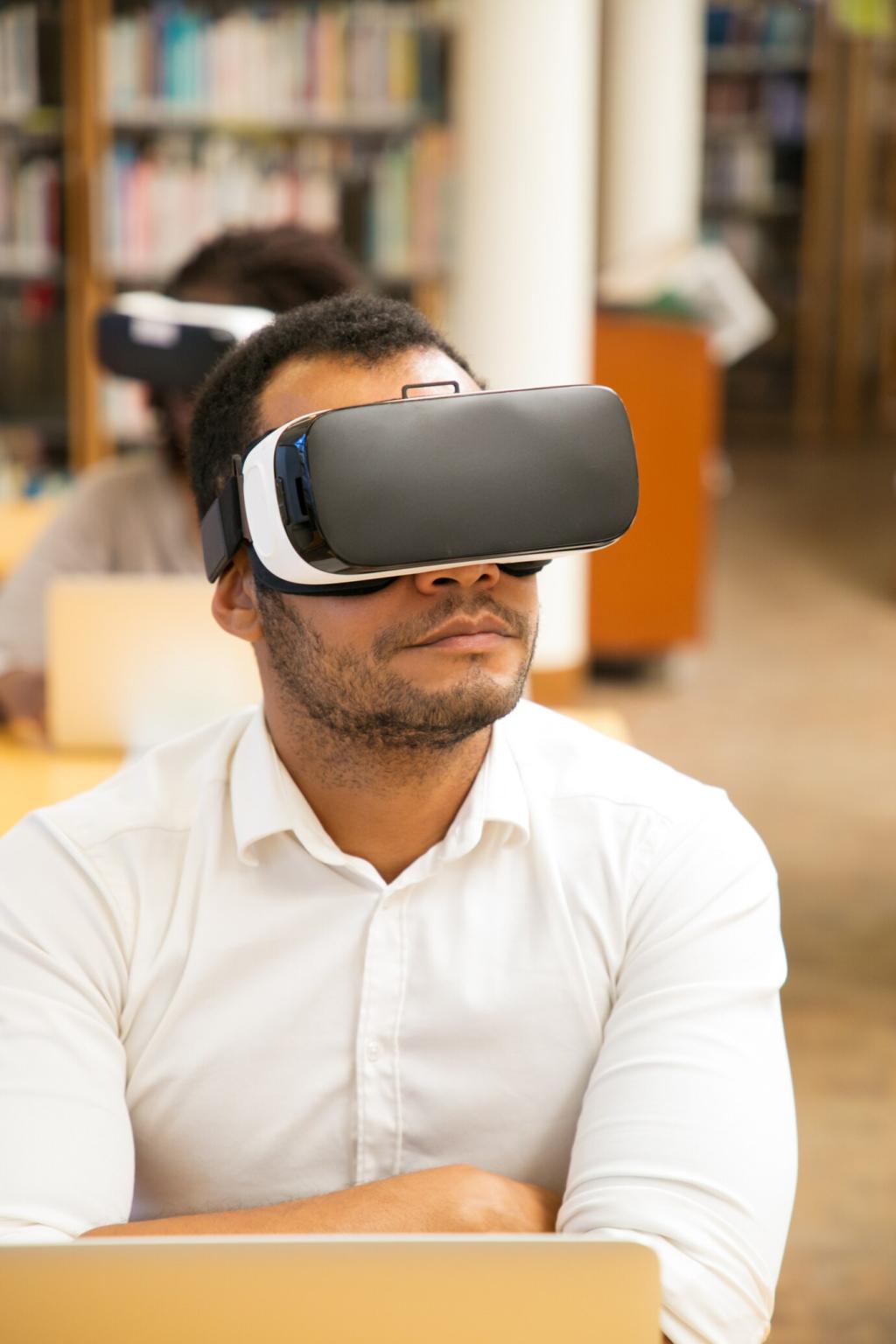

VR platforms enable students to partake in simulated conversations with lifelike avatars, removing the fear of embarrassment often experienced in real classrooms. Learners can practice ordering food in a virtual restaurant, asking for directions in an urban setting, or negotiating prices in a virtual market. Such simulations are designed to mimic real interactions, complete with natural soundscapes and varied linguistic challenges. This provides an emotionally safe space for learners to experiment with new vocabulary, grammar structures, and intonation, while receiving instant feedback. Over time, students build confidence and fluency that directly translate to improved performance in genuine face-to-face conversations.
Personalized Learning Journeys
Adaptive Learning Environments
One of the most powerful features of VR in language education is its ability to adapt dynamically to each learner’s strengths and weaknesses. Virtual environments can assess student performance in real-time and modify tasks to match proficiency levels, focusing on areas such as pronunciation, vocabulary recall, or listening comprehension. As students progress, the difficulty can increase, or aspects that require more attention will be revisited. This adaptive approach ensures that every learner receives the right level of challenge and support, fostering steady advancement and reducing frustration. Unlike rigid curricula, VR empowers students to take control of their own linguistic journey at their individual pace.
Customizable Scenarios for Specific Goals
VR systems can be tailored to suit the specific goals or professional needs of learners. For instance, a student aspiring to work in international business can practice negotiations or client meetings in a virtual boardroom, while another preparing for travel might navigate airports and hotel check-ins within the VR environment. This customization means that language learning becomes highly relevant and practical, allowing for targeted skill development. By catering to diverse objectives—be it academic, social, or professional—VR ensures that students not only learn the language but acquire the exact competencies they need to succeed in their chosen contexts.
Real-Time Progress Tracking
VR platforms often include built-in analytics that track user performance, highlighting strengths and pinpointing areas for improvement. As students navigate various scenarios, the software monitors aspects such as accuracy, response time, pronunciation, and comprehension. Teachers and students alike can review these insights to adjust learning strategies and set achievable goals. This data-driven approach encourages continuous reflection and motivates learners to strive for progress, turning language learning into a measurable and rewarding process. By making advancement visible and tangible, VR keeps students engaged and accountable—increasing the likelihood of long-term language mastery.

Enhanced Engagement and Motivation
By incorporating elements of play, competition, and achievement, VR brings the principles of gamification directly into the language classroom. Learners can earn points, unlock new scenarios, or achieve personal milestones as they progress through different linguistic challenges. This approach transforms repetitive drills into compelling missions or quests, making practice more enjoyable and less intimidating. The sense of accomplishment and friendly competition encourages consistent engagement, while failure becomes an opportunity to try again rather than a setback. Gamified VR experiences harness the intrinsic motivation that fuels effective, lifelong learning.
VR environments can foster greater participation, even among students who may be shy or hesitant to speak up in traditional classrooms. The anonymity and safety of interacting through avatars reduce social pressures, empowering all learners to join conversations, share ideas, and practice aloud. Additionally, many VR platforms are designed for collaborative learning, allowing students to work together to solve problems or complete tasks. These group activities promote teamwork and help learners develop important communication skills, as they must negotiate meaning, clarify understanding, and support one another using the target language.
For many language learners, anxiety about making mistakes or being judged by peers can be a significant barrier to progress. VR offers a supportive environment in which students can practice freely, outside the scrutiny of a physical classroom. Mistakes become part of the process and can be addressed without embarrassment or consequence. This reduction in anxiety encourages risk-taking and experimentation—crucial elements for developing language proficiency. By creating a space where learners feel comfortable, VR allows them to stretch their abilities, ultimately leading to increased confidence and fluency in real-world communication.